Minimal Django ORM
Django ORM is my favorite ORM. It is also why I like Django. To use Django ORM in different projects, I extract Django ORM functionality. This allows data processing.
Steps:
- Create a Django project and Django app. In this example, the project name is orm and the app name is app1
- Define data models in
models.py. Run make migrations and migrate to generate database tables - Remove extra files in the orm folder. Keep only
settings.pyand__init__.py - Create an ORM calling file in the project, such as
mini_orm.py
GitHub Address
cmd
git clone git@github.com:silentQQQ/mini-orm.gitProject Structure 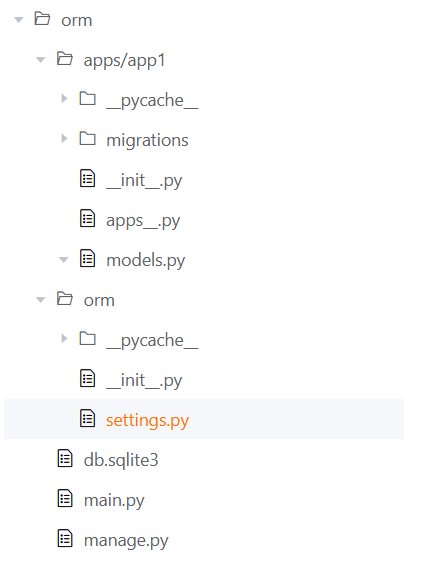
orm\orm\settings.py Description
You can remove extra configuration items. Keep only necessary items.
python
from pathlib import Path
import sys,os
# Build paths inside the project like this: BASE_DIR / 'subdir'.
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'apps'))
# SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret!
SECRET_KEY = '……'
# SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production!
DEBUG = True
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'apps.app1',
]
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': BASE_DIR / 'db.sqlite3',
}
}
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'zh-hans'
TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'
USE_I18N = True
USE_TZ = False
DEFAULT_AUTO_FIELD = 'django.db.models.BigAutoField'apps\app1\models.py
python
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
author = models.CharField(max_length=50,null=True, blank=True)
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2)
pub_date = models.DateField(null=True, blank=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.titleorm\main.py
python
import os
import sys
import django
from pathlib import Path
base_dir = str(Path(__file__).resolve().parent)
if base_dir.lower() not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(base_dir)
# Note! Change orm.settings to project_name.settings
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "orm.settings")
django.setup()
from apps.app1.models import Book
if __name__ == '__main__':
book = Book(title='moomboss blog', price=100, author='moomboss',pub_date='2021-11-01')
book.save()
print(book.pk)Done! You can now use Django ORM freely.